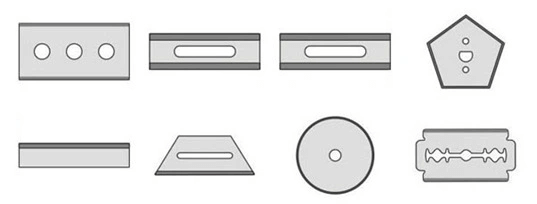
Ceramic Blades’ Characteristics
Let’s start with a definition of ceramics, because MIDDIA ceramics are not the delicate ceramics of common belief. They’re actually advanced ceramics, fine ceramics, or engineered ceramics, which are all terms for the same material. The material is made entirely of zirconium oxide. Zirconium oxide was developed in the 1950s as a result of breakthroughs in ceramic research. It has a wide range of applications.
A Flexible Material
Zirconium oxide has numerous advantages over steel, particularly in industrial settings. A zirconium oxide utility blade, unlike metal, is chemically inert. This eliminates the possibility of chemical reactions while cutting and provides a robust resistance against hazardous microorganisms. Ceramic never rusts, therefore it doesn’t need the same oils and lubricants as metal blades do to keep them from rusting prematurely.
Engineered ceramic utility blades have intrinsic features that serve industries as diverse as pulp and paper and aerospace:
Non-magnetic
Non-conductive
Non-sparking
Safe up to 1600 degrees Celsius
Chemically inert and non-contaminating
Non-reactive: impervious to acids and salt
Non-porous and chemically resistant
Oil and lubricant free
Never rusts
Hard as Nails (Harder, Actually)
Customers who are used to traditional blades are comparing two very different cutting experiences when they use MIDDIA instruments for the first time. Due to the various qualities of these materials, there are significant manufacturing variances between a MIDDIA ceramic blade and a steel blade. Because people are familiar with metal blade manufacturing procedures, most ceramic blade producers replicate them. These production procedures, on the other hand, were created for metal and its unique qualities. Hardness is the key distinction between advanced ceramics and metal.

Even the hardest steel is not as hard as zirconium oxide. What is the significance of hardness? Steel is sharpened to dangerous levels because of its relative softness; it dulls too rapidly. Unfortunately for safety, several ceramic blade makers ignored this crucial distinction and instead replicated the dangerously sharp edge of a metal blade, despite the fact that it isn’t necessary. Because of the hardness of zirconium oxide, MIDDIA was able to design a patent-pending manufacturing technique that produces a finger-friendly® edge.
The Finger-Friendly Ceramic Blade Edge from MIDDIA
Other businesses make razor-sharp ceramic blade knives, but MIDDIA was more concerned with safety. What amount of sharpness is required to cut most materials, we wondered? Steel blades are dangerously sharp because steel dulls so quickly, it turns out. To provide blades an acceptable operational lifespan, manufacturers must make them very sharp. This workaround puts productivity ahead of safety. Ceramics don’t require that workaround because they wear down so slowly.
While the intrinsic qualities of advanced ceramics initially drew the attention of kitchen knife manufacturers and later utility tool manufacturers, MIDDIA was the first to use zirconia’s hardness to create a grind that is actually safer to touch. That is what distinguishes a MIDDIA ceramic blade from others. We are so unique that we have over 100 patents.
The advantage for you to choose ceramic blade:
Sharpness: The material that make up a ceramic blade are very hard. So hard that they are the second hardest materal only to diamond. After the blade is sharpened, it will keep its razor sharp edge without wearing out or becoming dull. However metal blades require consistent sharpening.
Durability: Through our own testing and our customers’ feedback, our ceramic blade’s durability is 50 times longer than normal steel blade.
Rust: ceramic blade will not rust as metal blade will.
Blade can be customized as you required if you can send blade drawings or samples to us.
Related Products:
A. Cutting machinery Series (be used in cutting Fibre, tape, film etc).
Exact Cutting length, Less changing blade, higher producing efficiant
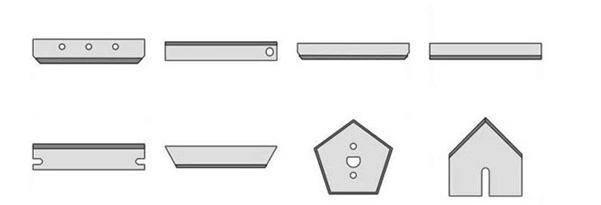
B. Textile blade
105mm Small Hole Rotary Cutter Round Circular Blade Ceramic Cutting Knife
No cause fibers to melt, longer usage
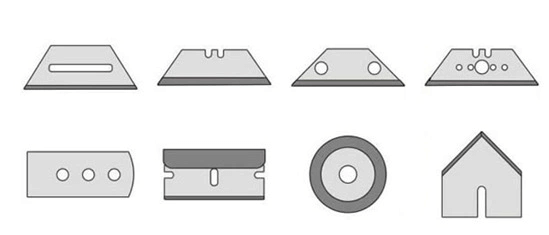
C. other type of blade
105mm Small Hole Rotary Cutter Round Circular Blade Ceramic Cutting Knife
Eletrostatic Prevention, Corrosion Resistion, much longer usage (50-100 times rather than steel)